
本文作者: slience_me
PS: 由于我有一台闲置的ThinkPad笔记本4c16g和一个低性能的云服务器2c2g,所以采用FRP去使用高性能的本地服务器
FRP内网穿透
一. Frp简介
frp(Fast Reverse Proxy)是一款高性能的反向代理应用,专为内网穿透设计。它支持多种协议,包括 TCP、UDP、HTTP、HTTPS 等,同时也具备 P2P(点对点)通信功能。通过在一个具有公网 IP 地址的中转节点上运行 frp,用户可以将内网服务暴露到公网,从而简化内网访问和管理的复杂性。
在实际应用中,frp 能够有效解决内网服务无法直接访问的问题。无论是个人用户在家搭建的 Web 服务,还是公司内部的开发环境,只需要在内网一端运行 frp 客户端,通过公网节点中转,即可实现内网服务的远程访问。这样的配置既安全可靠,又能大幅降低网络架构的复杂度。
除了常见的 Web 服务,frp 还支持一系列高级功能,包括:
- 通过端口映射将多个内网服务暴露到外部;
- 支持多种认证方式和加密传输,确保数据的安全性;
- 支持基于域名的路由分发,将不同域名映射到不同的内网服务;
- 提供自动重连和断点续传等稳定性和容错机制。
frp 的高效性和灵活性使其广泛应用于开发、运维、远程访问、物联网(IoT)设备接入等场景,是解决内网穿透需求的理想工具。
frp 项目地址:https://github.com/fatedier/frp
二. Frp特性
通过在具有公网 IP 地址的节点上部署 frp 服务端,用户可以轻松实现内网服务的公网穿透,同时享受以下多种专业功能特性:
- 多协议支持:客户端与服务端之间支持 TCP、QUIC、KCP、WebSocket 等多种协议,灵活应对不同的应用需求。
- TCP连接流式复用:采用流式复用技术,在单一连接中承载更多请求,显著降低连接建立时间和请求延迟。
- 负载均衡:支持代理组间的负载均衡,优化资源分配,提高服务性能和可靠性。
- 端口复用:多个服务可以通过同一个服务端端口进行暴露,节省端口资源,简化配置。
- P2P通信:支持 P2P 通信模式,流量绕过服务器中转,充分利用带宽资源,降低延迟。
- 原生客户端插件支持:提供多个原生客户端插件,例如静态文件查看、HTTPS/HTTP 协议转换、HTTP/SOCKS5 代理等,便于独立使用 frp 客户端完成特定任务。
- 高度可扩展的插件系统:服务端插件系统具备高度的扩展性,用户可以根据需求扩展功能。
- UI支持:提供服务端和客户端的图形界面(UI),使配置和管理更加简便直观。
这些特性使得 frp 在企业级应用、远程办公、云计算等领域具有广泛的应用场景,成为一款功能全面、稳定高效的内网穿透解决方案。
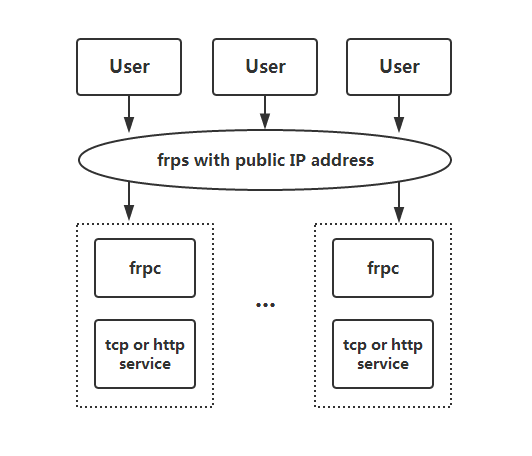
三. 架构与工作原理
frp 由两个核心组件构成:客户端 (frpc) 和 服务端 (frps)。通常情况下,服务端(frps)部署在具有公网 IP 地址的服务器上,而客户端(frpc)则运行在需要穿透的内网机器上。
4.1. 架构概述
在典型的应用场景中,内网机器通常无法直接与外网进行通信,因为它们没有公网 IP 地址。因此,这些机器上的服务(如 Web 服务、数据库、SSH 连接等)无法被外部用户直接访问。frp 通过建立客户端与服务端的连接,解决了这一问题。
- 服务端(frps):部署在公网可访问的服务器上,负责接收来自外部的请求,并将这些请求转发到连接到该服务端的内网客户端。服务端是整个架构的“网关”,它负责处理所有外部的网络请求。
- 客户端(frpc):运行在内网的机器上,负责与服务端建立连接并保持通信。客户端通过 frp 配置文件指定需要暴露的内网服务端口或应用,服务端接收到请求后,会通过已经建立的连接将请求转发到对应的内网服务。
4.2. 工作原理
- 连接建立:当客户端启动时,frpc 会通过预先配置好的设置与服务端(frps)建立一个稳定的长连接。这个连接通常是 TCP 或 UDP 类型,确保客户端和服务端之间的持续通信。
- 请求转发:外部用户访问服务端的公网 IP 地址时,frps 会根据请求的端口、协议或域名等信息,判断请求应当转发到哪个内网客户端。frps 通过已经建立的连接,将请求转发到相应的 frpc 客户端。
- 内网服务响应:内网的 frpc 客户端收到请求后,将请求转发到本地运行的服务(如 Web 服务器、数据库、SSH 等),并获取响应数据。之后,frpc 将响应数据通过已建立的长连接返回给服务端,服务端再将响应数据传递给外部用户。
- 双向通信:通过上述过程,外部用户能够像访问公网服务一样与内网服务进行通信,而内网服务也可以通过服务端与外部进行双向交互。整个过程中,内网机器无需直接暴露给外网,大大增强了安全性。
4.3. 特点与优势
- 简化网络架构:frp 将内网服务暴露到外网的过程完全透明,用户不需要进行复杂的端口映射或公网 IP 配置,极大简化了网络架构。
- 灵活的路由机制:服务端根据不同的请求信息(如端口、域名等),智能地将请求路由到相应的内网服务。通过域名和端口映射,用户可以将多个不同的内网服务暴露到公网。
- 高效的连接管理:frp 利用持久的连接和流式复用技术,最大限度地减少了连接的建立和中转延迟,使得内外网通信更加高效。
- 安全可靠:通过加密传输、身份认证等机制,frp 确保数据的安全性。此外,客户端与服务端的长连接和断点续传功能,使得即使在网络中断时也能够自动恢复,保障了稳定性。
四. 相关概念
4.1. 代理
在 frp 中,代理是指将内网服务暴露到公网的配置项。每个代理对应一个内网服务,负责将外部请求转发到该内网服务上。通过配置不同的代理,用户可以将多个内网服务同时暴露到外部网络。例如,用户可以同时将 Web 服务、SSH 服务和数据库服务通过不同的代理进行暴露。
一个客户端(frpc)可以同时配置多个代理,以满足多种不同的需求。这使得 frp 在复杂网络环境中,能够灵活地支持多种应用场景,帮助用户高效地管理和访问不同的内网服务。
4.2. 代理类型
frp 提供了多种代理类型,以适应不同的应用需求和使用场景。以下是一些常见的代理类型:
- TCP:提供传统的 TCP 端口映射功能。通过 TCP 代理,服务端可以根据请求的端口将流量转发到不同的内网服务。适用于需要在外网访问 TCP 协议的服务,如 Web 服务、SSH 等。
- UDP:与 TCP 代理类似,但专为 UDP 流量设计。UDP 代理可以将外部的 UDP 请求转发到内网的 UDP 服务,适用于实时通信、视频流、VoIP 等场景。
- HTTP:专门为 HTTP 协议设计的代理,支持通过 HTTP 请求转发流量。除了基本的端口映射功能外,HTTP 代理还可以进行额外的处理,如修改 Host Header 和增加访问鉴权功能。这对于 Web 应用场景非常有用,特别是在需要进行反向代理或负载均衡时。
- HTTPS:与 HTTP 代理类似,HTTPS 代理专为处理加密的 HTTPS 流量设计。它不仅能够转发 HTTPS 请求,还能提供 SSL/TLS 终止,帮助用户实现更加安全的内网服务暴露。
- STCP:提供安全的 TCP 内网代理。STCP 代理使用加密技术来保护数据传输,确保流量的安全性。在 STCP 代理中,数据通过加密隧道传输,因此无需在服务端暴露端口,也能保证通信的安全性。STCP 适用于需要高安全性的环境。
- SUDP:与 STCP 类似,SUDP 提供安全的 UDP 内网代理。它同样使用加密隧道来保护 UDP 流量,在无需在服务端暴露端口的情况下实现安全的 UDP 内网穿透。这对于需要加密保护的实时流量非常适用。
- XTCP:点对点(P2P)内网穿透代理。XTCP 代理不需要通过服务端进行流量中转,而是直接建立内网客户端之间的连接,利用点对点技术进行通信。通过 XTPC,内网服务可以在不通过公网服务器的情况下直接连接,减少延迟并提高带宽利用率。适用于需要高效、低延迟的通信场景。
- TCPMUX:提供服务端 TCP 端口的多路复用。通过 TCPMUX,多个内网服务可以共享同一个服务端端口。请求通过不同的标识符(如端口号或协议)来区分,从而访问不同的内网服务。这种方式能够显著减少对公网端口的需求,优化资源使用。
4.3. 代理类型选择
每种代理类型针对特定的需求和场景进行优化,因此用户应根据实际使用情况选择最合适的代理类型。例如,如果需要在外部访问 Web 服务,HTTP 或 HTTPS 代理将是最好的选择;如果需要实现加密传输和提高安全性,则 STCP 或 SUDP 会更为合适;对于高性能和低延迟的场景,XTCP 可以提供更优的体验。
通过合理选择代理类型,用户能够更加灵活地配置 frp,满足不同的网络穿透需求。
五. 安装
5.1. 需求描述
公司内部有一台位于内网的服务器 A 和一台拥有公网 IP 地址的云服务器 B。在内网服务器 A 上运行着 web服务,现在需要将 web服务通过公网暴露出来,以便外部用户能够通过云服务器 B 的公网 IP 进行访问。
PS: 我有一台位于内网的ThinkPad服务器A和一台拥有公网IP地址的云服务器B。在内网服务器A上运行着web服务,现在需要将web务通过公网暴露出来,以便外部用户能够通过云服务器 B 的公网 IP 进行访问。
5.2. 下载安装包
从官方 GitHub Release 页面下载 frp 的最新二进制安装包:frp Releases。截至目前,最新版本为 v0.54.0。Linux 版本的下载链接为:frp_0.54.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz。
5.3. 公网服务器部署 frp
当前服务器的公网IP:xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
(1) 上传安装包并解压
tar -xf frp_0.54.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz
mv frp_0.54.0_linux_amd64 frp
cd frp
# 目录结构
frp
├── frpc
├── frpc.toml
├── frps
├── frps.log
├── frps.toml
├── LICENSE
└── logs
└── frps.log
(2) 修改配置
编辑 frps.toml 配置文件,设置服务端的相关参数。
vim frps.toml
配置内容:
现在需要详细的介绍一下:
bindAddr:服务端监听地址,用于接收 frpc 的连接,默认监听 0.0.0.0
bindPort:服务端监听端口,默认值为 7000
auth.method:鉴权方式,可选值为 token 或 oidc,默认为 token
auth.token:在 method 为 token 时生效,客户端需要设置一样的值才能鉴权通过
webServer:用于服务器端的web界面显示
# 服务绑定的IP与端口
bindAddr = "0.0.0.0"
bindPort = 7000
# Web Dashboard 配置
webServer.addr = "0.0.0.0"
webServer.port = 7500
webServer.user = "admin"
webServer.password = "admin"
# 启用 Prometheus 监控指标
enablePrometheus = true
# Token 权限验证,需与客户端配置一致
auth.method = "token"
auth.token = "123456"
# 日志配置
log.to = "/app/frp/logs/frps.log"
log.level = "info"
log.maxDays = 3
(3) 创建日志目录
mkdir /app/frp/logs
(4) 启动服务
-
命令行方式启动:
./frps -c ./frps.toml -
后台启动:
nohup ./frps -c ./frps.toml &> /dev/null & -
使用 systemd 启动:
- 创建
frps.service启动文件:
vim /etc/systemd/system/frps.service - 创建
配置文件内容:
[Unit]
# 服务名称,可自定义
Description = frp server
After = network.target syslog.target
Wants = network.target
[Service]
Type = simple
# 启动 frps 的命令,需修改为您的 frps 安装路径
ExecStart = /app/frp/frps -c /app/frp/frps.toml
[Install]
WantedBy = multi-user.target
- 启动服务:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start frps
(5) 开放防火墙
去
云服务器后台的安全组开放端口
(6) 测试服务端后台
访问:
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:7500用户名:
admin密码:
admin
5.4. 内网服务器部署 frp
当前服务器的内网IP:127.0.0.1
(1) 上传安装包并解压
tar -xf frp_0.54.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz
mv frp_0.54.0_linux_amd64 frp
cd frp
# 目录结构
frp
├── conf.d
│└── purecolor.toml
├── frpc
├── frpc.toml
├── frps
├── frps.toml
├── LICENSE
└── logs
└── frpc.log
(2) 创建代理配置目录与日志存储目录
mkdir logs conf.d
(3) 修改配置
编辑 frpc.toml 配置文件,设置客户端的相关参数。
vim frpc.toml
配置内容:
现在需要详细的介绍一下:
serverAddr:连接服务端的地址
serverPort:连接服务端的端口,默认为 7000
auth.method:鉴权方式,可选值为 token 或 oidc,默认为 token
auth.token:在 method 为 token 时生效,客户端需要设置一样的值才能鉴权通过
webServer:用于服务器端的web界面显示
./conf.d/:这里面存放不同的代理配置
# 配置公网服务器上 frp 服务的 IP 与端口
serverAddr = "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx" # 填写公网服务器 IP
serverPort = 7000
# Web Dashboard 配置
webServer.addr = "0.0.0.0"
webServer.port = 7400
webServer.user = "admin"
webServer.password = "admin"
# 日志配置
log.to = "/app/frp/logs/frpc.log"
log.level = "info"
log.maxDays = 3
# Token 权限验证,需与服务端配置一致
auth.method = "token"
auth.token = "123456"
# 代理配置,这里使用引用文件的方式
includes = ["./conf.d/*.toml"]
编辑代理配置文件 webapp.toml,将内网 Jenkins 服务暴露到公网。
vim ./conf.d/webapp.toml
配置内容:
[[proxies]]
name = "mywebapp" # 代理名称
type = "tcp" # 代理类型,TCP
localIP = "127.0.0.1" # 内网服务的 IP
localPort = 8080 # 服务监听的端口(即内网web项目服务的端口)
remotePort = 8500 # 公网服务器上监听的端口(设置服务器所对应的端口)
(内网)127.0.0.1:8080 -> (公网) xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8500
(4) 启动服务
- 命令行方式启动:
./frpc -c ./frpc.toml
- 后台启动:
nohup ./frpc -c ./frpc.toml &> /dev/null &
- 使用 systemd 启动:
- 创建
frpc.service启动文件:
vim /etc/systemd/system/frpc.service
配置文件内容:
[Unit]
# 服务名称,可自定义
Description = frp client
After = network.target syslog.target
Wants = network.target
[Service]
Type = simple
# 启动 frpc 的命令,需修改为您的 frpc 安装路径
ExecStart = /app/frp/frpc -c /app/frp/frpc.toml
[Install]
WantedBy = multi-user.target
- 启动服务:
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start frpc
(5) 开放防火墙
去
本地服务器的开放端口
ufw allow xxxx
(6) 测试服务端后台
访问:
http://127.0.0.1:7400用户名:
admin密码:
admin
5.5. 访问测试汇总
- 在浏览器中访问公网服务器的 web 服务:
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8500即可访问到内网的 web服务。 - 公网服务器的 Web Dashboard:
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:7500登录界面将显示为admin用户,密码为admin。 - 公网服务器的 Prometheus 监控指标:
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:7500/metrics用于查看服务的实时监控数据。
注意: 如果公网服务器启用了安全组或防火墙,请确保相应的端口已开放。
六. 附录:
从官网下载了服务端与客户端的全配置文件,仅供参考
6.1. 服务端全配置文件
frps_full_example.toml
# This configuration file is for reference only. Please do not use this configuration directly to run the program as it may have various issues.
# A literal address or host name for IPv6 must be enclosed
# in square brackets, as in "[::1]:80", "[ipv6-host]:http" or "[ipv6-host%zone]:80"
# For single "bindAddr" field, no need square brackets, like `bindAddr = "::"`.
bindAddr = "0.0.0.0"
bindPort = 7000
# udp port used for kcp protocol, it can be same with 'bindPort'.
# if not set, kcp is disabled in frps.
kcpBindPort = 7000
# udp port used for quic protocol.
# if not set, quic is disabled in frps.
# quicBindPort = 7002
# Specify which address proxy will listen for, default value is same with bindAddr
# proxyBindAddr = "127.0.0.1"
# quic protocol options
# transport.quic.keepalivePeriod = 10
# transport.quic.maxIdleTimeout = 30
# transport.quic.maxIncomingStreams = 100000
# Heartbeat configure, it's not recommended to modify the default value
# The default value of heartbeatTimeout is 90. Set negative value to disable it.
# transport.heartbeatTimeout = 90
# Pool count in each proxy will keep no more than maxPoolCount.
transport.maxPoolCount = 5
# If tcp stream multiplexing is used, default is true
# transport.tcpMux = true
# Specify keep alive interval for tcp mux.
# only valid if tcpMux is true.
# transport.tcpMuxKeepaliveInterval = 60
# tcpKeepalive specifies the interval between keep-alive probes for an active network connection between frpc and frps.
# If negative, keep-alive probes are disabled.
# transport.tcpKeepalive = 7200
# transport.tls.force specifies whether to only accept TLS-encrypted connections. By default, the value is false.
transport.tls.force = false
# transport.tls.certFile = "server.crt"
# transport.tls.keyFile = "server.key"
# transport.tls.trustedCaFile = "ca.crt"
# If you want to support virtual host, you must set the http port for listening (optional)
# Note: http port and https port can be same with bindPort
vhostHTTPPort = 80
vhostHTTPSPort = 443
# Response header timeout(seconds) for vhost http server, default is 60s
# vhostHTTPTimeout = 60
# tcpmuxHTTPConnectPort specifies the port that the server listens for TCP
# HTTP CONNECT requests. If the value is 0, the server will not multiplex TCP
# requests on one single port. If it's not - it will listen on this value for
# HTTP CONNECT requests. By default, this value is 0.
# tcpmuxHTTPConnectPort = 1337
# If tcpmuxPassthrough is true, frps won't do any update on traffic.
# tcpmuxPassthrough = false
# Configure the web server to enable the dashboard for frps.
# dashboard is available only if webServer.port is set.
webServer.addr = "127.0.0.1"
webServer.port = 7500
webServer.user = "admin"
webServer.password = "admin"
# webServer.tls.certFile = "server.crt"
# webServer.tls.keyFile = "server.key"
# dashboard assets directory(only for debug mode)
# webServer.assetsDir = "./static"
# Enable golang pprof handlers in dashboard listener.
# Dashboard port must be set first
webServer.pprofEnable = false
# enablePrometheus will export prometheus metrics on webServer in /metrics api.
enablePrometheus = true
# console or real logFile path like ./frps.log
log.to = "./frps.log"
# trace, debug, info, warn, error
log.level = "info"
log.maxDays = 3
# disable log colors when log.to is console, default is false
log.disablePrintColor = false
# DetailedErrorsToClient defines whether to send the specific error (with debug info) to frpc. By default, this value is true.
detailedErrorsToClient = true
# auth.method specifies what authentication method to use authenticate frpc with frps.
# If "token" is specified - token will be read into login message.
# If "oidc" is specified - OIDC (Open ID Connect) token will be issued using OIDC settings. By default, this value is "token".
auth.method = "token"
# auth.additionalScopes specifies additional scopes to include authentication information.
# Optional values are HeartBeats, NewWorkConns.
# auth.additionalScopes = ["HeartBeats", "NewWorkConns"]
# auth token
auth.token = "12345678"
# oidc issuer specifies the issuer to verify OIDC tokens with.
auth.oidc.issuer = ""
# oidc audience specifies the audience OIDC tokens should contain when validated.
auth.oidc.audience = ""
# oidc skipExpiryCheck specifies whether to skip checking if the OIDC token is expired.
auth.oidc.skipExpiryCheck = false
# oidc skipIssuerCheck specifies whether to skip checking if the OIDC token's issuer claim matches the issuer specified in OidcIssuer.
auth.oidc.skipIssuerCheck = false
# userConnTimeout specifies the maximum time to wait for a work connection.
# userConnTimeout = 10
# Only allow frpc to bind ports you list. By default, there won't be any limit.
allowPorts = [
{ start = 2000, end = 3000 },
{ single = 3001 },
{ single = 3003 },
{ start = 4000, end = 50000 }
]
# Max ports can be used for each client, default value is 0 means no limit
maxPortsPerClient = 0
# If subDomainHost is not empty, you can set subdomain when type is http or https in frpc's configure file
# When subdomain is test, the host used by routing is test.frps.com
subDomainHost = "frps.com"
# custom 404 page for HTTP requests
# custom404Page = "/path/to/404.html"
# specify udp packet size, unit is byte. If not set, the default value is 1500.
# This parameter should be same between client and server.
# It affects the udp and sudp proxy.
udpPacketSize = 1500
# Retention time for NAT hole punching strategy data.
natholeAnalysisDataReserveHours = 168
# ssh tunnel gateway
# If you want to enable this feature, the bindPort parameter is required, while others are optional.
# By default, this feature is disabled. It will be enabled if bindPort is greater than 0.
# sshTunnelGateway.bindPort = 2200
# sshTunnelGateway.privateKeyFile = "/home/frp-user/.ssh/id_rsa"
# sshTunnelGateway.autoGenPrivateKeyPath = ""
# sshTunnelGateway.authorizedKeysFile = "/home/frp-user/.ssh/authorized_keys"
[[httpPlugins]]
name = "user-manager"
addr = "127.0.0.1:9000"
path = "/handler"
ops = ["Login"]
[[httpPlugins]]
name = "port-manager"
addr = "127.0.0.1:9001"
path = "/handler"
ops = ["NewProxy"]
6.2. 客户端全配置文件
frpc_full_example.toml
# This configuration file is for reference only. Please do not use this configuration directly to run the program as it may have various issues.
# your proxy name will be changed to {user}.{proxy}
user = "your_name"
# A literal address or host name for IPv6 must be enclosed
# in square brackets, as in "[::1]:80", "[ipv6-host]:http" or "[ipv6-host%zone]:80"
# For single serverAddr field, no need square brackets, like serverAddr = "::".
serverAddr = "0.0.0.0"
serverPort = 7000
# STUN server to help penetrate NAT hole.
# natHoleStunServer = "stun.easyvoip.com:3478"
# Decide if exit program when first login failed, otherwise continuous relogin to frps
# default is true
loginFailExit = true
# console or real logFile path like ./frpc.log
log.to = "./frpc.log"
# trace, debug, info, warn, error
log.level = "info"
log.maxDays = 3
# disable log colors when log.to is console, default is false
log.disablePrintColor = false
auth.method = "token"
# auth.additionalScopes specifies additional scopes to include authentication information.
# Optional values are HeartBeats, NewWorkConns.
# auth.additionalScopes = ["HeartBeats", "NewWorkConns"]
# auth token
auth.token = "12345678"
# oidc.clientID specifies the client ID to use to get a token in OIDC authentication.
# auth.oidc.clientID = ""
# oidc.clientSecret specifies the client secret to use to get a token in OIDC authentication.
# auth.oidc.clientSecret = ""
# oidc.audience specifies the audience of the token in OIDC authentication.
# auth.oidc.audience = ""
# oidc.scope specifies the permissions of the token in OIDC authentication if AuthenticationMethod == "oidc". By default, this value is "".
# auth.oidc.scope = ""
# oidc.tokenEndpointURL specifies the URL which implements OIDC Token Endpoint.
# It will be used to get an OIDC token.
# auth.oidc.tokenEndpointURL = ""
# oidc.additionalEndpointParams specifies additional parameters to be sent to the OIDC Token Endpoint.
# For example, if you want to specify the "audience" parameter, you can set as follow.
# frp will add "audience=<value>" "var1=<value>" to the additional parameters.
# auth.oidc.additionalEndpointParams.audience = "https://dev.auth.com/api/v2/"
# auth.oidc.additionalEndpointParams.var1 = "foobar"
# Set admin address for control frpc's action by http api such as reload
webServer.addr = "127.0.0.1"
webServer.port = 7400
webServer.user = "admin"
webServer.password = "admin"
# Admin assets directory. By default, these assets are bundled with frpc.
# webServer.assetsDir = "./static"
# Enable golang pprof handlers in admin listener.
webServer.pprofEnable = false
# The maximum amount of time a dial to server will wait for a connect to complete. Default value is 10 seconds.
# transport.dialServerTimeout = 10
# dialServerKeepalive specifies the interval between keep-alive probes for an active network connection between frpc and frps.
# If negative, keep-alive probes are disabled.
# transport.dialServerKeepalive = 7200
# connections will be established in advance, default value is zero
transport.poolCount = 5
# If tcp stream multiplexing is used, default is true, it must be same with frps
# transport.tcpMux = true
# Specify keep alive interval for tcp mux.
# only valid if tcpMux is enabled.
# transport.tcpMuxKeepaliveInterval = 60
# Communication protocol used to connect to server
# supports tcp, kcp, quic, websocket and wss now, default is tcp
transport.protocol = "tcp"
# set client binding ip when connect server, default is empty.
# only when protocol = tcp or websocket, the value will be used.
transport.connectServerLocalIP = "0.0.0.0"
# if you want to connect frps by http proxy or socks5 proxy or ntlm proxy, you can set proxyURL here or in global environment variables
# it only works when protocol is tcp
# transport.proxyURL = "http://user:passwd@192.168.1.128:8080"
# transport.proxyURL = "socks5://user:passwd@192.168.1.128:1080"
# transport.proxyURL = "ntlm://user:passwd@192.168.1.128:2080"
# quic protocol options
# transport.quic.keepalivePeriod = 10
# transport.quic.maxIdleTimeout = 30
# transport.quic.maxIncomingStreams = 100000
# If tls.enable is true, frpc will connect frps by tls.
# Since v0.50.0, the default value has been changed to true, and tls is enabled by default.
transport.tls.enable = true
# transport.tls.certFile = "client.crt"
# transport.tls.keyFile = "client.key"
# transport.tls.trustedCaFile = "ca.crt"
# transport.tls.serverName = "example.com"
# If the disableCustomTLSFirstByte is set to false, frpc will establish a connection with frps using the
# first custom byte when tls is enabled.
# Since v0.50.0, the default value has been changed to true, and the first custom byte is disabled by default.
# transport.tls.disableCustomTLSFirstByte = true
# Heartbeat configure, it's not recommended to modify the default value.
# The default value of heartbeatInterval is 10 and heartbeatTimeout is 90. Set negative value
# to disable it.
# transport.heartbeatInterval = 30
# transport.heartbeatTimeout = 90
# Specify a dns server, so frpc will use this instead of default one
# dnsServer = "8.8.8.8"
# Proxy names you want to start.
# Default is empty, means all proxies.
# start = ["ssh", "dns"]
# Specify udp packet size, unit is byte. If not set, the default value is 1500.
# This parameter should be same between client and server.
# It affects the udp and sudp proxy.
udpPacketSize = 1500
# Additional metadatas for client.
metadatas.var1 = "abc"
metadatas.var2 = "123"
# Include other config files for proxies.
# includes = ["./confd/*.ini"]
[[proxies]]
# 'ssh' is the unique proxy name
# If global user is not empty, it will be changed to {user}.{proxy} such as 'your_name.ssh'
name = "ssh"
type = "tcp"
localIP = "127.0.0.1"
localPort = 22
# Limit bandwidth for this proxy, unit is KB and MB
transport.bandwidthLimit = "1MB"
# Where to limit bandwidth, can be 'client' or 'server', default is 'client'
transport.bandwidthLimitMode = "client"
# If true, traffic of this proxy will be encrypted, default is false
transport.useEncryption = false
# If true, traffic will be compressed
transport.useCompression = false
# Remote port listen by frps
remotePort = 6001
# frps will load balancing connections for proxies in same group
loadBalancer.group = "test_group"
# group should have same group key
loadBalancer.groupKey = "123456"
# Enable health check for the backend service, it supports 'tcp' and 'http' now.
# frpc will connect local service's port to detect it's healthy status
healthCheck.type = "tcp"
# Health check connection timeout
healthCheck.timeoutSeconds = 3
# If continuous failed in 3 times, the proxy will be removed from frps
healthCheck.maxFailed = 3
# Every 10 seconds will do a health check
healthCheck.intervalSeconds = 10
# Additional meta info for each proxy. It will be passed to the server-side plugin for use.
metadatas.var1 = "abc"
metadatas.var2 = "123"
# You can add some extra information to the proxy through annotations.
# These annotations will be displayed on the frps dashboard.
[proxies.annotations]
key1 = "value1"
"prefix/key2" = "value2"
[[proxies]]
name = "ssh_random"
type = "tcp"
localIP = "192.168.31.100"
localPort = 22
# If remotePort is 0, frps will assign a random port for you
remotePort = 0
[[proxies]]
name = "dns"
type = "udp"
localIP = "114.114.114.114"
localPort = 53
remotePort = 6002
# Resolve your domain names to [serverAddr] so you can use http://web01.yourdomain.com to browse web01 and http://web02.yourdomain.com to browse web02
[[proxies]]
name = "web01"
type = "http"
localIP = "127.0.0.1"
localPort = 80
# http username and password are safety certification for http protocol
# if not set, you can access this customDomains without certification
httpUser = "admin"
httpPassword = "admin"
# if domain for frps is frps.com, then you can access [web01] proxy by URL http://web01.frps.com
subdomain = "web01"
customDomains = ["web01.yourdomain.com"]
# locations is only available for http type
locations = ["/", "/pic"]
# route requests to this service if http basic auto user is abc
# routeByHTTPUser = abc
hostHeaderRewrite = "example.com"
requestHeaders.set.x-from-where = "frp"
healthCheck.type = "http"
# frpc will send a GET http request '/status' to local http service
# http service is alive when it return 2xx http response code
healthCheck.path = "/status"
healthCheck.intervalSeconds = 10
healthCheck.maxFailed = 3
healthCheck.timeoutSeconds = 3
[[proxies]]
name = "web02"
type = "https"
localIP = "127.0.0.1"
localPort = 8000
subdomain = "web02"
customDomains = ["web02.yourdomain.com"]
# if not empty, frpc will use proxy protocol to transfer connection info to your local service
# v1 or v2 or empty
transport.proxyProtocolVersion = "v2"
[[proxies]]
name = "tcpmuxhttpconnect"
type = "tcpmux"
multiplexer = "httpconnect"
localIP = "127.0.0.1"
localPort = 10701
customDomains = ["tunnel1"]
# routeByHTTPUser = "user1"
[[proxies]]
name = "plugin_unix_domain_socket"
type = "tcp"
remotePort = 6003
# if plugin is defined, localIP and localPort is useless
# plugin will handle connections got from frps
[proxies.plugin]
type = "unix_domain_socket"
unixPath = "/var/run/docker.sock"
[[proxies]]
name = "plugin_http_proxy"
type = "tcp"
remotePort = 6004
[proxies.plugin]
type = "http_proxy"
httpUser = "abc"
httpPassword = "abc"
[[proxies]]
name = "plugin_socks5"
type = "tcp"
remotePort = 6005
[proxies.plugin]
type = "socks5"
username = "abc"
password = "abc"
[[proxies]]
name = "plugin_static_file"
type = "tcp"
remotePort = 6006
[proxies.plugin]
type = "static_file"
localPath = "/var/www/blog"
stripPrefix = "static"
httpUser = "abc"
httpPassword = "abc"
[[proxies]]
name = "plugin_https2http"
type = "https"
customDomains = ["test.yourdomain.com"]
[proxies.plugin]
type = "https2http"
localAddr = "127.0.0.1:80"
crtPath = "./server.crt"
keyPath = "./server.key"
hostHeaderRewrite = "127.0.0.1"
requestHeaders.set.x-from-where = "frp"
[[proxies]]
name = "plugin_https2https"
type = "https"
customDomains = ["test.yourdomain.com"]
[proxies.plugin]
type = "https2https"
localAddr = "127.0.0.1:443"
crtPath = "./server.crt"
keyPath = "./server.key"
hostHeaderRewrite = "127.0.0.1"
requestHeaders.set.x-from-where = "frp"
[[proxies]]
name = "plugin_http2https"
type = "http"
customDomains = ["test.yourdomain.com"]
[proxies.plugin]
type = "http2https"
localAddr = "127.0.0.1:443"
hostHeaderRewrite = "127.0.0.1"
requestHeaders.set.x-from-where = "frp"
[[proxies]]
name = "secret_tcp"
# If the type is secret tcp, remotePort is useless
# Who want to connect local port should deploy another frpc with stcp proxy and role is visitor
type = "stcp"
# secretKey is used for authentication for visitors
secretKey = "abcdefg"
localIP = "127.0.0.1"
localPort = 22
# If not empty, only visitors from specified users can connect.
# Otherwise, visitors from same user can connect. '*' means allow all users.
allowUsers = ["*"]
[[proxies]]
name = "p2p_tcp"
type = "xtcp"
secretKey = "abcdefg"
localIP = "127.0.0.1"
localPort = 22
# If not empty, only visitors from specified users can connect.
# Otherwise, visitors from same user can connect. '*' means allow all users.
allowUsers = ["user1", "user2"]
# frpc role visitor -> frps -> frpc role server
[[visitors]]
name = "secret_tcp_visitor"
type = "stcp"
# the server name you want to visitor
serverName = "secret_tcp"
secretKey = "abcdefg"
# connect this address to visitor stcp server
bindAddr = "127.0.0.1"
# bindPort can be less than 0, it means don't bind to the port and only receive connections redirected from
# other visitors. (This is not supported for SUDP now)
bindPort = 9000
[[visitors]]
name = "p2p_tcp_visitor"
type = "xtcp"
# if the server user is not set, it defaults to the current user
serverUser = "user1"
serverName = "p2p_tcp"
secretKey = "abcdefg"
bindAddr = "127.0.0.1"
# bindPort can be less than 0, it means don't bind to the port and only receive connections redirected from
# other visitors. (This is not supported for SUDP now)
bindPort = 9001
# when automatic tunnel persistence is required, set it to true
keepTunnelOpen = false
# effective when keepTunnelOpen is set to true, the number of attempts to punch through per hour
maxRetriesAnHour = 8
minRetryInterval = 90
# fallbackTo = "stcp_visitor"
# fallbackTimeoutMs = 500
6.3. 官网示例配置参考
英文:https://github.com/fatedier/frp?tab=readme-ov-file#example-usage
中文:https://gofrp.org/zh-cn/docs/examples/
参考链接:
文档信息
- 本文作者:slience_me
- 本文链接:https://slienceme.cn/2025/02/19/frp/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)